Suche:
- # Artistry
- # Biology
- # Chemistry
- # Ecological
- # Economy
- # English
- # Foreign Language
- # Geography
- # German
- # Health
- # History
- # Informatik
- # Latin
- # Mathematics
- # Media Education
- # Music
- # Physics
- # Politics / Civics
- # Preschool
- # Primary School
- # Religion
- # Society
- # Sports
- # Technology
- # Training of Teachers
- # Vocational Education
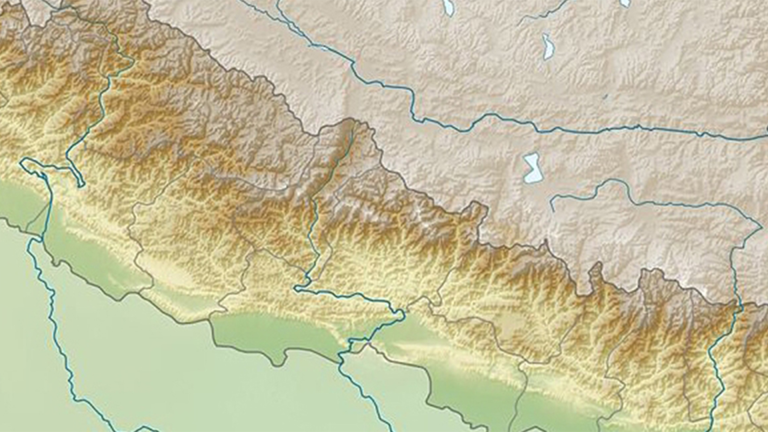
Tibet
Tibet, the so-called »Roof of the World«, is a vast highland in Central Asia. Hidden behind huge mountain ranges, the highest plateau of earth together with its inhabitants, the Tibetans, is little known to the rest of the world. The »country of the snow lion«, as the historical Tibet is also called, is comprised of the three big provinces Ü-Tsang, Kham and Amdo and several smaller ones encompassing an area of 2.5 million square kilometres. China, however, incorporated all of Amdo and large parts of Kham into the adjacent Chinese provinces. The remaining area was given the name »Tibet Autonomous Region«.
Learn moreLignite
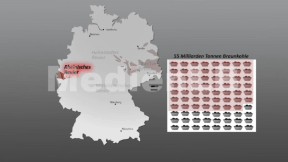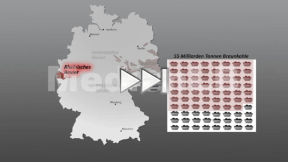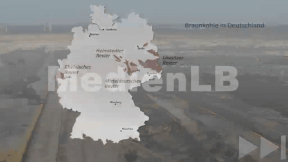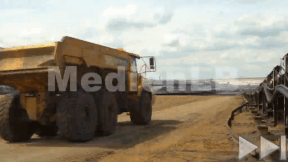
Lignite, or brown coal, is an important energy carrier for providing Germany with electric power. In 2017 some 23 % of the country’s electricity was still obtained from lignite. German mining activities are centred in the Rhenish lignite fields to the west of Cologne. In the new eastern states, lignite is mainly extracted in the mining areas of Central Germany and Lusatia.
Learn moreGlobalisation
A visit to the weekly market. Here they lie peacefully side by side: pears and apples from local regions next to exotic fruits such as kiwi, lychee, papaya and mango. What was an exotic rarity not so long ago is meanwhile offered throughout the whole year. So today there is a wide range of products from all over the world. The reason for this variety of products is what has become widely known under the term of globalisation.
Learn moreSaarland
One of the small States of the Federal Republic of Germany is also represented in this film series. A turbulent history in a border situation between two power blocs, coal and steel, structural change, services and nanotechnology. Join us on a short trip through Saarland!
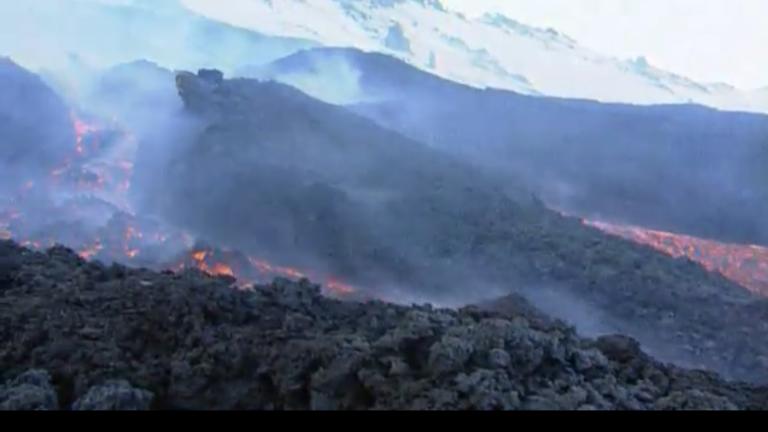
Learn moreVolcanos
When volcanos are mentioned in the media, this is usually in connection with devastating eruptions, which come with massive damage and a great number of victims. However, volcanos can also be quite useful – either as tourist attractions or as suppliers of valuable resources. This DVD offers an introduction to volcanism. For this purpose, the following subjects are treated in four film clips: “Structure of Volcanos” – there can be considerable structural differences among the firemountains; “Types of Eruption” – depending on the composition of the magma, explosive or effusive eruptions occur; “Moderate Activities” – in between and after larger eruptions a volcano never rests completely; “Mining Products and their Use” – the materials discharged are diverse and often useful. When choosing the examples of volcanic regions (the Eifel and South Italy), the proven didactic principle “from near to far” was observed. In view of the relative proximity of the regions, the film is suitable for the preparation of field trips, which are expressly to be encouraged.
Learn moreGreen Tourism
Whereas a few decades ago many countries on this earth could be reached under the most difficult conditions only, an unlimited number of travel destinations all over the world are open to people today. Package tours, long-haul flights even to the most distant regions, are available to almost anyone willing to travel.
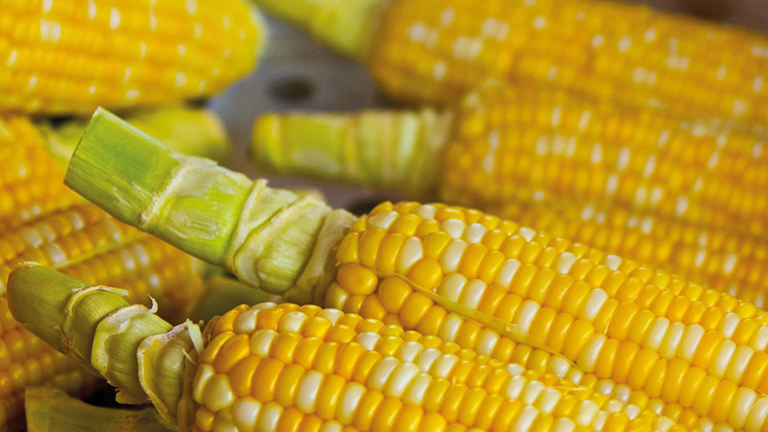
Learn moreMais
Mais ist eine der ältesten Kulturpflanzen der Welt. Ursprünglich kommt er aus Mittelamerika und war dort als Nahrung unentbehrlich. Christoph Kolumbus hat einige dieser Getreidepflanzen auf seinen Schiffen mit nach Europa genommen, so verbreitete sich die Pflanze recht schnell.
Learn moreHesse
The federal state of Hesse is located in the centre of Germany and borders on the federal states of Lower Saxony, Thuringia, Bavaria, Baden-Wuerttemberg, Rhineland-Palatinate and North Rhine-Westphalia. Especially South Hesse, with the international financial and commercial centre as well as traffic hub Frankfurt on the Main, is one of the most densely populated and economically powerful regions of Germany.
Learn moreHigh-tech Locations
The satellite dishes of the first terrestrial communications site on German ground in Raisting near the Ammersee have been a symbol of high-tech in Bavaria for decades.
Learn moreBavaria
The free state of Bavaria is one of the most diverse states of the Federal Republic of Germany. Amidst the Alps with the Alpine Foothills and the Frankenwald and Lake Constance in the southwest, there are various regions that considerably differ from each other with regard to landscape as well as to economic basis. From a historical point of view, too, today’s Bavaria has evolved from individual states like the Duchy of Bavaria and several dioceses and free imperial cities like, for instance, Freising and Augsburg. Particularly interesting is the rise of the former agrarian state, which was to a large extent structurally weak, to one of the leading federal states in terms of economy and technology in the period from World War II until today. With its culture and numerous cultural treasures, Bavaria attracts tourists from all over the world, which contri- buted to the emergence of a service-oriented economy. Due to the modified, modular regional-studies approach, the DVD is suitable from the 5th to the 10th year of school.
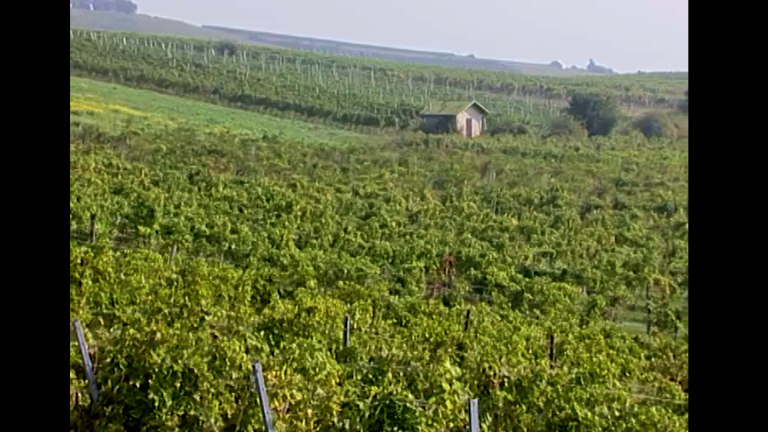
Learn moreWine-Growing
The film starts with a short, simple overview of the importance of viticulture in Germany and Austria and the most famous wine regions in both countries. Then it goes on to discuss the most important conditions (soil, solar radiation) and forms of cultivation (terraces and vineyards on the plains) as well as the most widely spread types of grapes in Germany and Austria. In the main part of the film, pupils of a primary school accompany a wine-grower throughout the working year, watching him at work in the vineyard: form of the vine, work in winter (pruning, fruitbearing vines, substitute vines) turning cut-off vines into chaff, additional jobs (hammering in sticks, tightening wires, fastening fruit-bearing vines), removal of the earth from the grafting spots, pest control, cultivation of green manure crops, removal of surplus shoots, blossoming, weed removal, fighting nematodes (threadworms) biologically by cultivating daikon radish and, finally, harvesting. Apart from the manual harvest – where young and old people join in – also the use of harvesters is described.
Learn more