55502602
Alkalimetalle
In 11 interaktiven Aufgaben und Videos werden die Eigenschaften und Verwendung von Alkalimetallen vermittelt und anschließend abgefragt.
Das Medium bietet H5P-Aufgaben an, die ohne zusätzliche Software verwendbar sind.
Durch interaktive Aufgabentypen wird das audiovisuelle und interaktive Lernen einfach.
Lernen macht jetzt Spaß!
Included Tasks
- I Alkalimetalle - Video mit interaktiven Aufgaben
- II 1.Hauptgruppe des PSE - interaktive Aufgabe
- III Alkalimetalle - Bildpaare finden
- IV Flammenfärbung der Alkalimetalle - Video mit Aufgaben
- V Physikalische Eigenschaften - interaktive Aufgabe
- VI Verwendung von Alkalimetallen - interaktive Aufgabe
- VII Reaktion von Natrium mit Chlor - interaktive Aufgabe
- VIII Natrium-Kalium-Wissen - interaktive Flashcards
- IX Farbige Silvesterraketen 1 - Lückentext
- X farbige Silvesterraketen 2 - interaktive Aufgabe
- XI Alkalimetalle - Quizfragen
Curriculum-centred and oriented towards educational standards
Matching
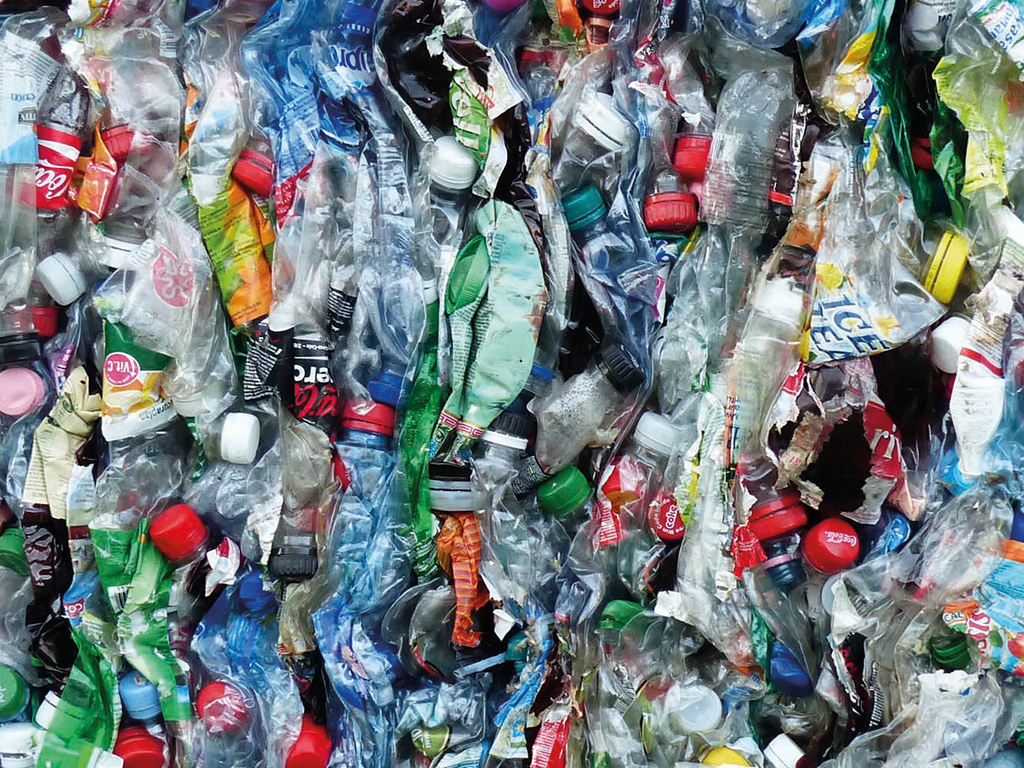
Plastic
Plastic has been around for not longer than roughly 100 years, and the synthetic material is a brilliant invention. Its production is cheap, it can take almost any possible form, it is light-weight, versatile and, above all, inexpensive.
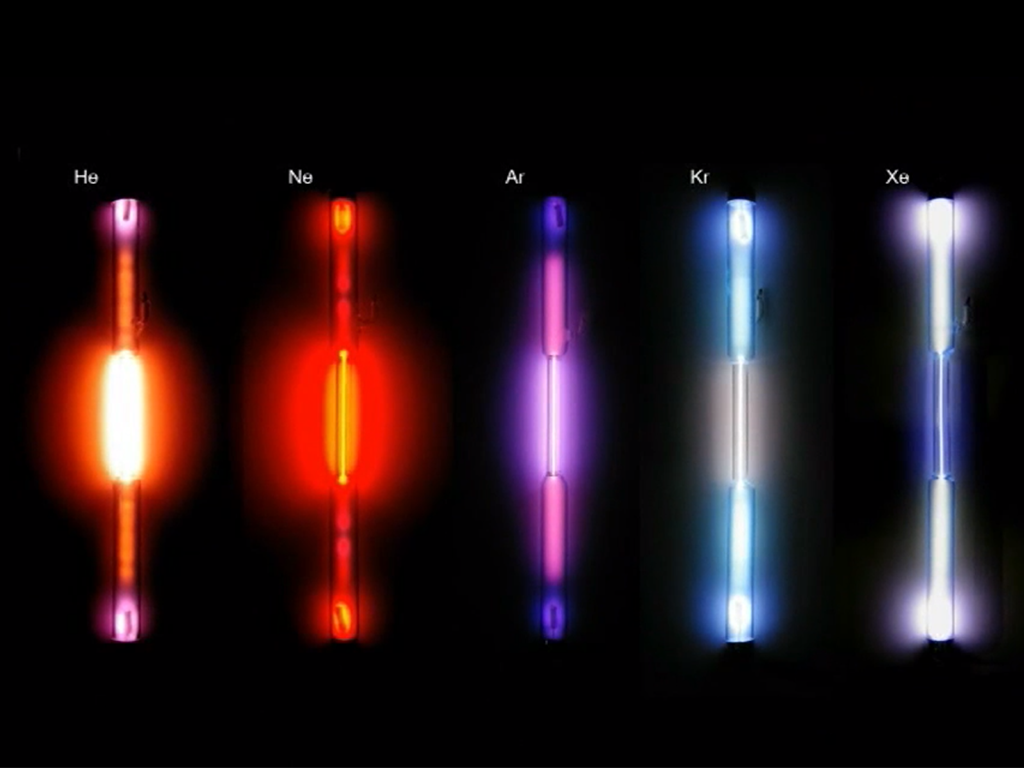
Noble Gases
Xenon, Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton and the radioactive Radon belong to the noble gases. These form the family of noble gases as the elements of the eighth group of the periodic table. All of them are colourless and odourless, non-inflammable and non-toxic. Their most striking chemical property is their inertness. This can be explained by their electron arrangement, termed noble gas configuration and represents a particularly stable and therefore low-energy state. The noble gases are to be found in scant amounts in our air from which they are also distilled. Helium is mainly extracted from natural gas. In everyday life, we encounter noble gases for example as shielding, filling or buoyant gases and in fluorescent tubes. The shell model describes the structure of the atoms. It is based on the distribution of electrons in restricted areas at a fixed distance around the core of the atom.