History
History

46500915 / 55500671
Napoleon Bonaparte
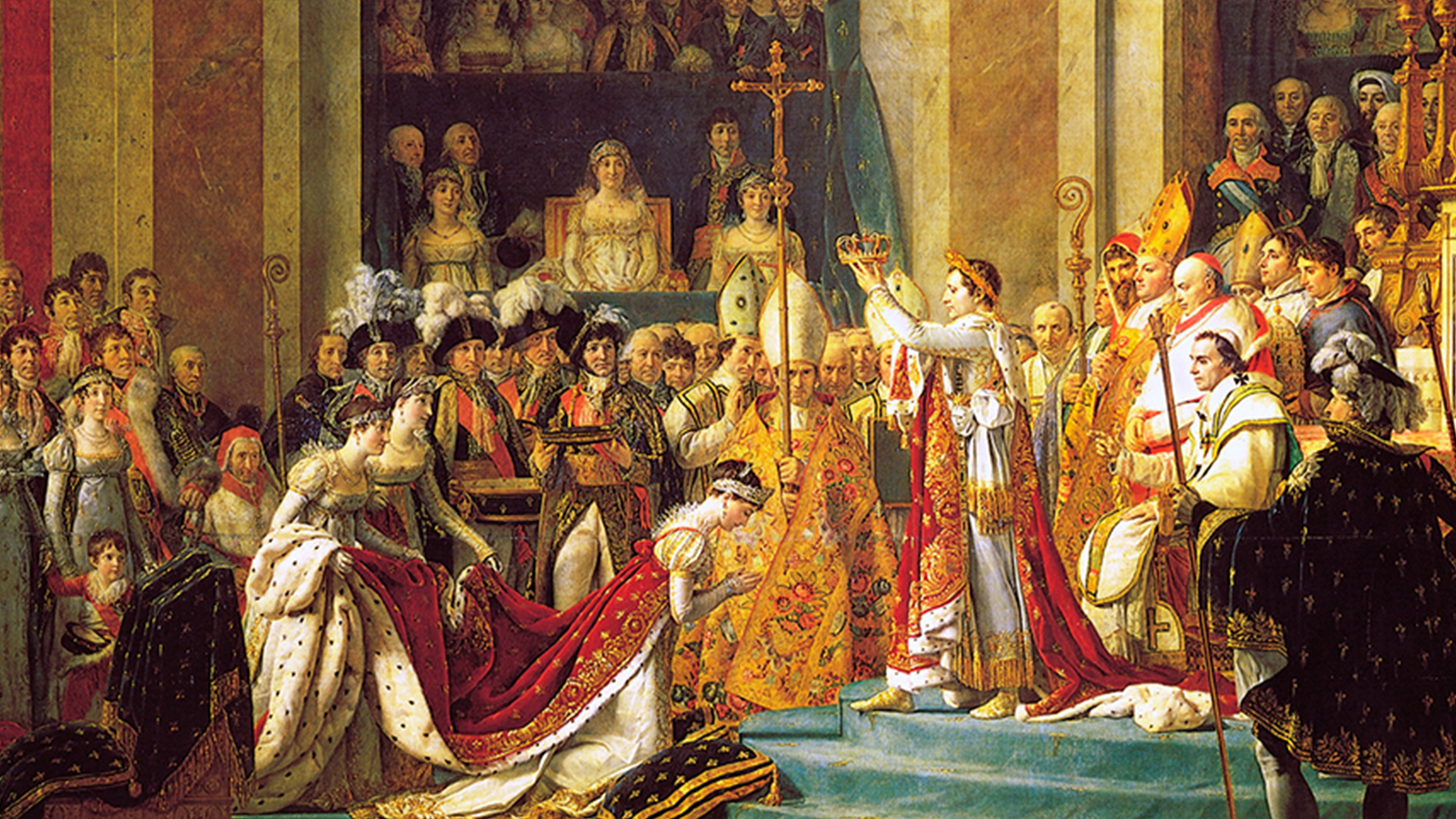
Rise and Fall
Napoleon Bonaparte shaped France and Europe like no other.
He was innovator and mastermind, strategist and emperor.
Between genius and megalomania he rose very high and fell very low in the end.
He raised France to its greatest glory and almost plunged it into ruin.
His achievements have been effective up to the present day.
Europe is almost inconceivable without his reforms and he even left his mark in the legislations of many European states — in the German Basic Law as well.
Napoleon Bonaparte was born in Corsica on August 15, 1769.
He was the fourth of thirteen children of a family from the lower nobility.
His father Carlo Bonaparte was a lawyer.
Corsica is an island in the Mediterranean Sea, which had originally belonged to Genoa and been sold to France as late as in 1768.
So, many Corsicans fought for independence from France at the time.
Napoleon’s father, too, supported the resistance against France and fought for an independent Corsica.
But those who resisted France lost all their possessions.
Napoleon’s father decided to support the French because he had to provide for a large family and could not afford resistance anymore.
Due to their defection to the side of the French, the Bonaparte family got back their possessions.
Shaped by his Corsican environment, his pride and sense of honour and revenge corresponded to the ideal of masculinity of his time.
Very early on, his greatest interest focused on the military.
He loved everything related to it.
At the age of nine, Napoleon received a scholarship for the military school at Brienne in France.
As a Corsican, he was only a “second-class” Frenchman at the academy.
This prodded his ambition all the more. He always wanted to win. This did not make for popularity, so he was considered an outsider. Nevertheless, his ambition and leadership qualities attracted attention there, too.

Curriculum-centred and oriented towards educational standards
Matching
Rights and Obligations
Three girls of different ages: Anna is 17, Paula 15 and Lena 13. Before the law, their respective ages have consequences – because children and adolescents have different rights and also obligations.
Seal of approval
Quality seals such as the "Bio-Siegel", "Blauer Engel", "Stiftung Warentest" and up to 1,000 other seals represent characteristics such as sustainability, health or safety with regard to a product, a service or even a company.